Union Budget 2026 Explained: Sector-Wise Allocation, Key Highlights & What It Means for India
The Union Budget 2026–27, presented on 1 February 2026 by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, lays out the government’s financial and economic priorities for the coming year. Unlike short-term relief–focused budgets, Budget 2026 is clearly designed as a long-term, growth-oriented roadmap, with heavy investment in infrastructure, defence, manufacturing, rural development, and social sectors.
In this blog, we provide a clear, informative, and sector-wise breakdown of Budget 2026, including exact allocation amounts, key announcements, and their real-world impact on citizens and the economy.
Budget 2026: Big Picture Overview
Budget 2026 focuses on:
- Accelerating economic growth
- Strengthening infrastructure and connectivity
- Boosting manufacturing and self-reliance
- Maintaining fiscal discipline
- Supporting agriculture, healthcare, and education
Key Budget Numbers at a Glance:
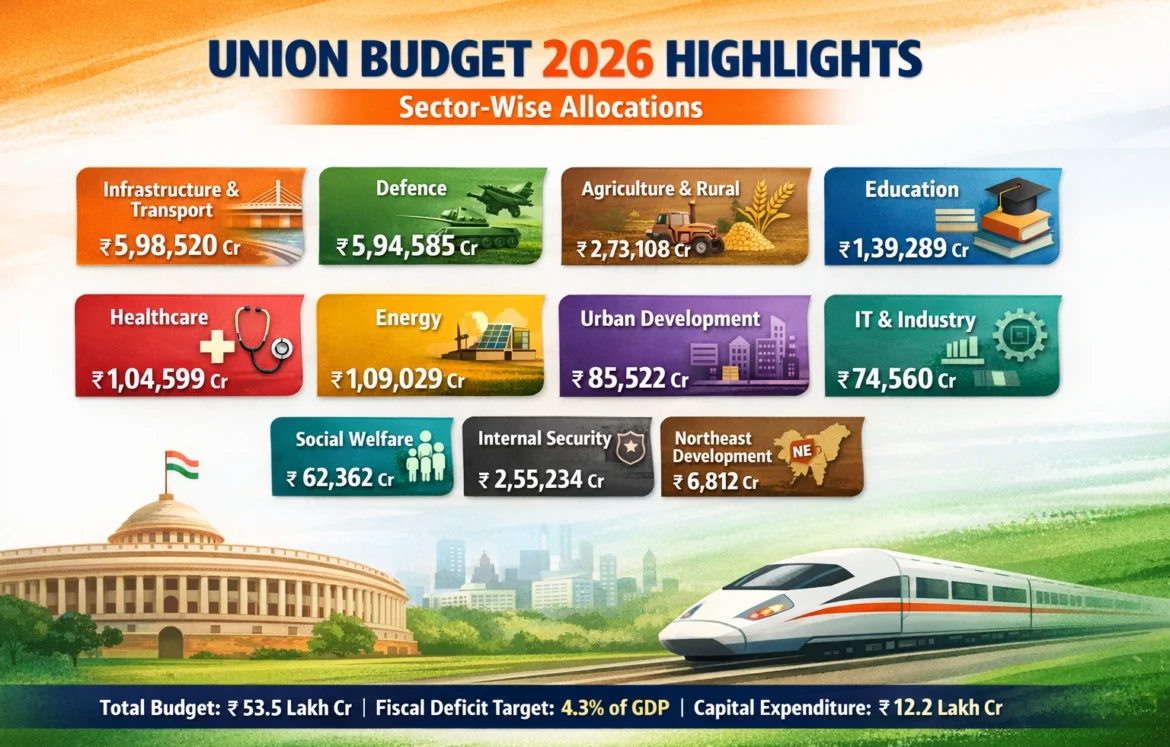
- Total Expenditure: ~₹53.5 lakh crore
- Capital Expenditure (Capex): ~₹12.2 lakh crore
- Fiscal Deficit Target: ~4.3% of GDP
The strong capital expenditure push indicates the government’s intent to drive job creation, investment, and long-term productivity.
Infrastructure & Transport: The Biggest Priority
Infrastructure and transport receive the highest allocation in Budget 2026, highlighting the government’s focus on connectivity and logistics efficiency.
Allocation:
- Total Transport Sector: ₹5,98,520 crore
- Road Transport & Highways: ~₹3,10,000 crore
- Railways: ~₹2,77,830 crore
Key Focus Areas:
- Expansion of national highways and expressways
- Modernisation of railways and freight corridors
- Development of high-speed rail corridors
- Inland waterways and logistics parks
Impact:
This investment boosts real estate, construction, cement, steel, logistics, and employment, while improving travel and goods movement across India.
Defence: Strengthening National Security
Allocation:
- Defence Budget: ₹5,94,585 crore
Focus Areas:
- Defence modernisation
- Indigenous manufacturing of defence equipment
- Border security and strategic preparedness
Impact:
Supports “Make in India” in defence, improves national security, and creates opportunities for domestic defence manufacturers.
Agriculture & Rural Development: Supporting Bharat
Allocation:
- Rural Development: ₹2,73,108 crore
- Agriculture & Allied Activities: ₹1,62,671 crore
Focus Areas:
- Farmer income support through technology
- Irrigation and rural infrastructure
- Agri-processing and value-addition
- Livestock, fisheries, and storage facilities
Impact:
Moves beyond subsidies towards income growth, productivity, and rural employment.
Education & Skill Development: Investing in Human Capital
Allocation:
- Education: ₹1,39,289 crore
Focus Areas:
- School education and teacher training
- Higher education and research
- Skill development aligned with industry needs
- Digital education platforms
Impact:
Builds a future-ready workforce and strengthens India’s long-term competitiveness.
Healthcare & Family Welfare: Strengthening Social Infrastructure
Allocation:
- Health & Family Welfare: ₹1,04,599 crore
Focus Areas:
- Public healthcare infrastructure
- Reduced customs duty on essential medicines
- Disease prevention and health programs
- Medical research and medical tourism
Impact:
Improves access to healthcare and reduces treatment costs for citizens.
Energy & Power: Securing the Future
Allocation:
- Energy Sector: ₹1,09,029 crore
Focus Areas:
- Renewable energy
- Power transmission and grid expansion
- Energy security and sustainability
Impact:
Supports India’s transition toward clean and reliable energy.
Urban Development & Social Welfare
Allocation:
- Urban Development: ₹85,522 crore
- Social Welfare: ₹62,362 crore
Focus Areas:
- Urban infrastructure and housing
- Sanitation and city development
- Welfare of vulnerable and marginalised groups
Impact:
Improves quality of life in both urban and semi-urban areas.
Industry, Technology & Innovation
Allocation:
- IT & Telecom: ₹74,560 crore
- Commerce & Industry: ₹70,296 crore
- Scientific Departments (R&D): ₹55,756 crore
Focus Areas:
- Digital infrastructure
- Semiconductor and electronics manufacturing
- MSME and startup support
- Research and innovation
Impact:
Encourages technology-led growth, innovation, and job creation.
Internal Security & Governance
Allocation:
- Home Affairs: ₹2,55,234 crore
- Tax Administration: ₹45,500 crore
- Finance Ministry: ₹20,649 crore
Focus Areas:
- Internal security and policing
- Efficient tax systems
- Financial governance
Other Key Allocations
- External Affairs: ₹22,119 crore
- North-East Development: ₹6,812 crore
These allocations support diplomacy, regional development, and balanced national growth.
Positives of Budget 2026
- Strong infrastructure-led growth strategy
- Clear long-term economic vision
- High capital expenditure
- Support for manufacturing and MSMEs
- Focus on employment generation
Concerns & Criticism
- Limited immediate tax relief for the middle class
- Benefits may take time to reach the ground level
- Inflation concerns remain
Final Verdict: Is Budget 2026 Growth-Driven?
The Union Budget 2026 is a future-focused and investment-driven budget. Instead of short-term giveaways, the government has prioritised infrastructure, defence, manufacturing, and human capital to build a stronger and more resilient economy.
While some sections may have expected immediate relief, Budget 2026 clearly aims to lay the foundation for sustainable growth and job creation over the coming years.
In short, Budget 2026 is about building tomorrow, not just managing today.
